A wide range of metal and plastic material for CNC machining, with applications in multiple industries.
CNC Machining > Material
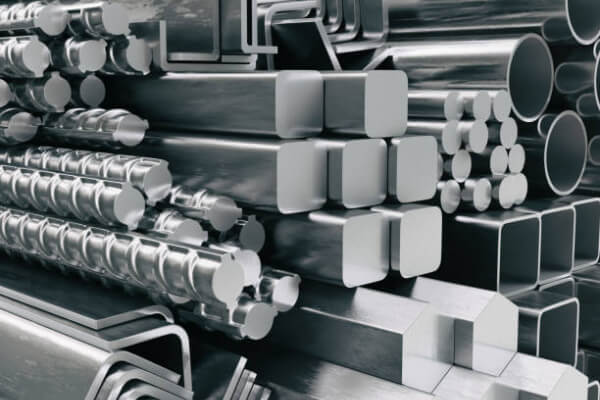
Choosing the right material is crucial for CNC machining because material properties directly impact part performance and machining difficulty. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Application Requirements: Determine the environment and function the part will be used for. Consider mechanical properties, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, etc.
2. Material Characteristics: Understand the properties of various materials, including strength, hardness, toughness, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, etc., to determine the most suitable material.
3. Machining Performance: Consider the machining performance of the material, including ease of machining, machinability, weldability, etc., to ensure it meets CNC machining requirements
4. Cost and Availability: Consider the cost and availability of the material to ensure you can obtain the required material within budget.
5. Design Requirements: Select the material based on design requirements, including size, geometry, surface finish, etc.
6. Standards and Specifications: Follow applicable standards and specifications to ensure the selected material meets industry standards and customer requirements.
| Name | Description | Price | ||
 | Aluminum | High machinability and ductility, good strength-to-weight ratio. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Aluminum materials |
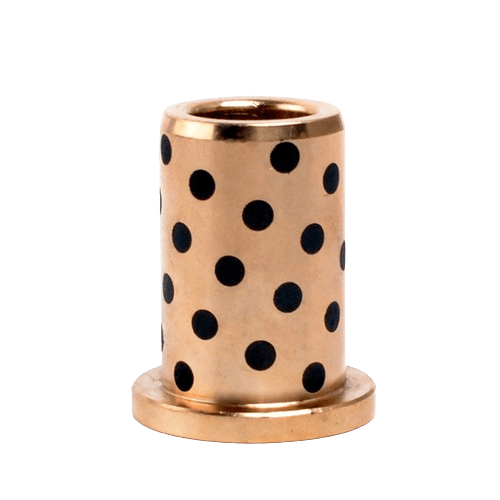 | Brass | Low friction, excellent electrical conductivity, golden appearance. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Brass materials |
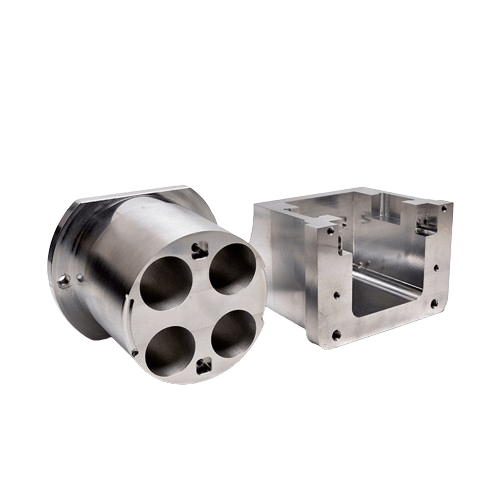 | Steel | Strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Steel materials |
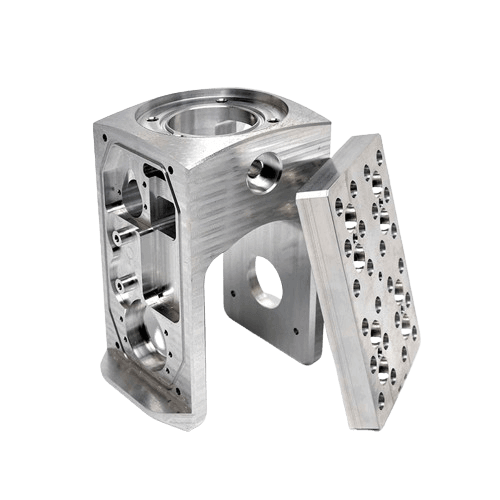 | Stainless Steel | High tensile strength, corrosion and temperature resistant. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Stainless Steel materials |
 | Titanium | Excellent strength to weight ratio, used in aerospace, automotive and medical industries. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Titanium materials |
 | ABS | Common thermoplastic, impact resistant, easy to machine. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse ABS materials |
 | Acrylic | Optical clarity, impact resistance, and weatherability | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Acrylic materials |
 | Garolite G-10 | High strength, low moisture absorption, and high level of electrical insulation and chemical resistance. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse G-10 materials |
 | HDPE | High strength-to-density ratio, chemical resistance, and durability | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse HDPE materials |
 | Nylon | Excellent mechanical properties, thermal, chemical and abrasion resistant. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse Nylon materials |
 | PC/Polycarbonate | High toughness, excellent impact strength, transparent. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse PC materials |
 | PEEK | High-performance thermoplastic, very high strength, thermal and chemical resistant. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse PEEK materials |
 | POM/Delrin acetal | High stiffness, high accuracy, low friction, easy to machine. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse POM materials |
 | PPS | Exceptional chemical resistance, high temperature stability, and mechanical strength | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse PPS materials |
 | PTFE | Low friction, chemical and thermal resistant. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse PTFE materials |
 | PVC | Excellent chemical and weather resistance and good toughness. | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse PVC materials |
 | UHMW | High abrasion resistance, low coefficient of friction, excellent impact strength, and self-lubricating properties | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse UHMW materials |
 | ULTEM | Exceptional strength, high temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and excellent chemical resistance | $ $ $ $ $ | Browse ULTEM materials |
1.Required strength
Consider what type of strength characteristics are needed for the part, such as tensile strength, compression strength, or yield strength. The material choice will depend on the intended application and the load that the part will be subjected to.
2.Wear resistance
Consider whether the part will be subjected to abrasion or friction and choose a material that can withstand those conditions for the required duration of use.
3.Corrosion resistance
Consider whether the part will be exposed to harsh environments that could cause corrosion or rust over time, and choose a material that can resist or minimize these effects.
4.Machinability
Consider whether the material will be easy to machine and produce good surface finishes without excessive tool wear or breakage.
5.Cost
Consider the cost of the material, taking into account how it will affect the overall cost of the part, including machining costs, finishing costs, and any subsequent assembly requirements it may have.
The cost of plastic CNC machining depends on the complexity and size of the part as well as the type of plastic that is used. These variables will influence the type of machine that is required, the time it takes to produce the part, and the cost of the raw material.
We use machine learning algorithms to calculate the exact cost of any machinable part directly from a CAD file, based on millions of CNC machining orders we’ve previously processed. Simply upload a CAD file to generate a quote: Get an instant CNC machining quote.
Metal machining is a manufacturing process that involves cutting a piece of raw metal until a final desired shape or object remains. With CNC metal machining, unwanted geometry is cut from a raw block of metal, bit by bit with a computer numerically controlled (CNC) milling or turning cutting tool, very precisely and allows complex parts to be produced with great accuracy.